Methane, a potent greenhouse gas with a global warming potential dozens of times higher than carbon dioxide, is frequently leaked throughout various operational stages in the oil and gas industry.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the oil and gas industry is responsible for 62% of emissions within the energy sector, totaling 80 million tons, while global methane emissions in 2023 amounted to 349 million tons, of which energy sector accounts for 36.8%.
To reduce the methane emissions in the oil and gas industry, stricter and more detailed regulatory requirements are being implemented globally.
Region | Action | Key Points | Date |
United States | U.S. Methane Emissions Reduction Action Plan | Adopt all available tools—commonsense regulations, catalytic financial incentives, transparency and disclosure of actionable data, and public and private partnerships—to identify and reduce methane emissions. | Nov-21 |
United States | Inflation Reduction Act | Provide new authorities under Section 136 of the Clean Air Act to reduce methane emissions from the petroleum and natural gas sector, and require methane emission charges. | Aug-22 |
United States | 40 CFR Part 60- Standards of Performance for New, Reconstructed, and Modified Sources and Emissions Guidelines for Existing Sources: Oil and Natural Gas Sector Climate Review | Aim to reduce air pollution emissions from the Crude Oil and Natural Gas source category. | May-24 |
United States | 40 CFR Part 98 - Greenhouse Gas Reporting Rule: Revisions and Confidentiality Determinations for Petroleum and Natural Gas Systems | Apply to a wide range of oil and gas facilities operated by the petroleum production, gas transmission, and utility industries. | July-24 |
Europe | European Union Methane Action Plan | Aim to reduce methane emissions, improve air quality, and reinforce the EU’s global leadership in the fight against climate change. | Oct-20 |
Europe | European Union (EU) Methane Regulation | As part of the European Green Deal and the EU's Methane Strategy, the first EU-wide legislation that aims at reducing global methane emissions. | June 2024 (expected) |
China | Methane Emission Control Action Plan | Highlight as key priorities the improvement of the monitoring, reporting, and verification system for methane emissions, as well as methane-emissions control actions in the energy, agriculture, and waste sectors. | Nov-23 |

Under this text, monitoring and reducing methane emissions is essential in compliant with regulatory requirements in the oil and gas industry. The IEA estimates that 75% of methane emissions in the oil and gas industry can be reduced by existing technologies and best practices, with 40% of reductions achievable at zero net cost, which indicates that it is vital for oil and gas operators to actively develop and adopt advanced methane detection solutions, to effectively minimize its emissions during various operation stages within the industry.
In the oil and gas industry, remote field monitoring by Cubic Sensor and Instrument Co.,Ltd. plays a vital role in tracking emissions, particularly methane. Oil and gas production sites are often located in remote areas, far from urban areas, and cover large areas. Remote field monitoring enables real-time methane detection of emissions from distant site, allowing operators to identify methane leaks or abnormal emissions quickly.

In the oil and gas industry, gas flaring is a common practice used to manage associated gas that cannot be economically or safely utilized. However, gas flaring results in the release of significant amounts of methane and other greenhouse gases, which have profound impacts on the environment and climate change. Therefore, monitoring gas flaring is of critical importance.

In the oil and gas industry, pipeline continuous methane monitoring solutions are crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient transport of natural gas, which contains methane—a potent greenhouse gas. Any leaks or ruptures in the pipelines can lead to the release of large amounts of methane into the atmosphere, contributing significantly to climate change and posing serious safety hazards.

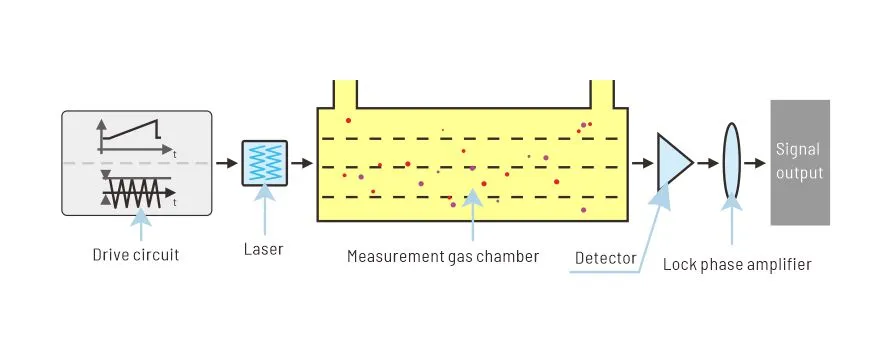
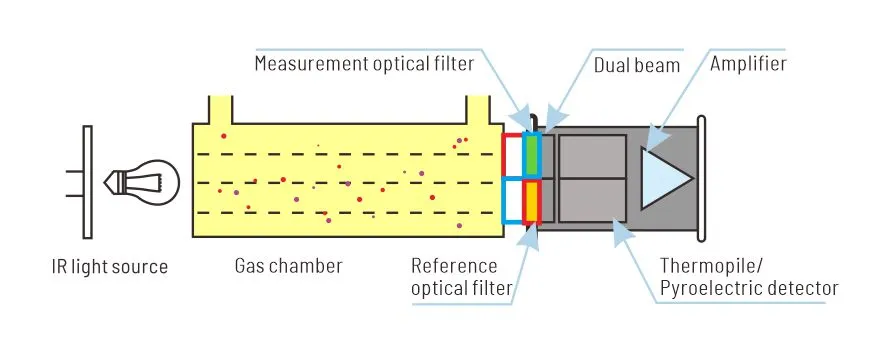
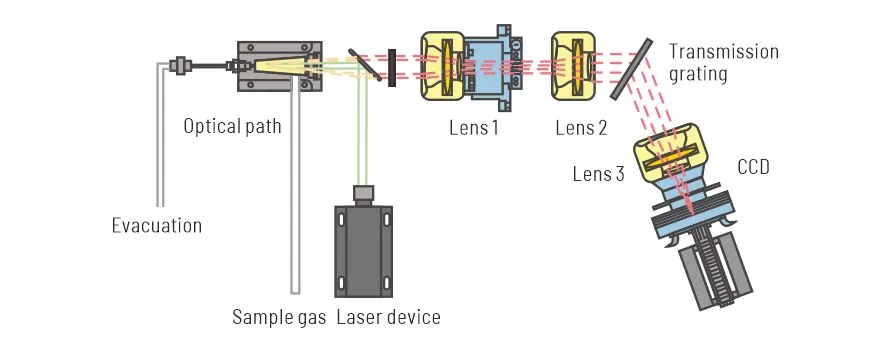
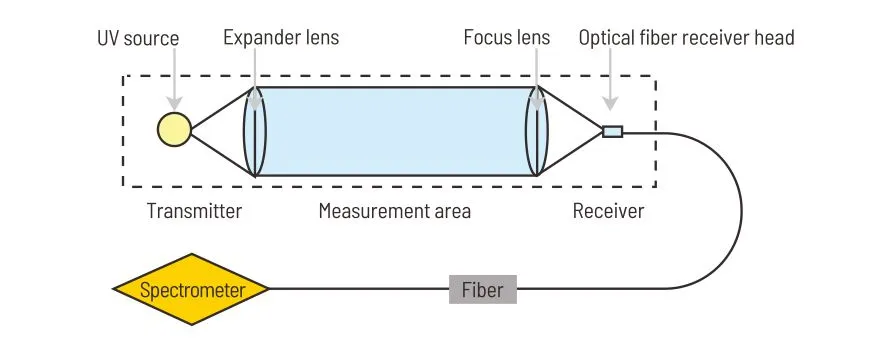
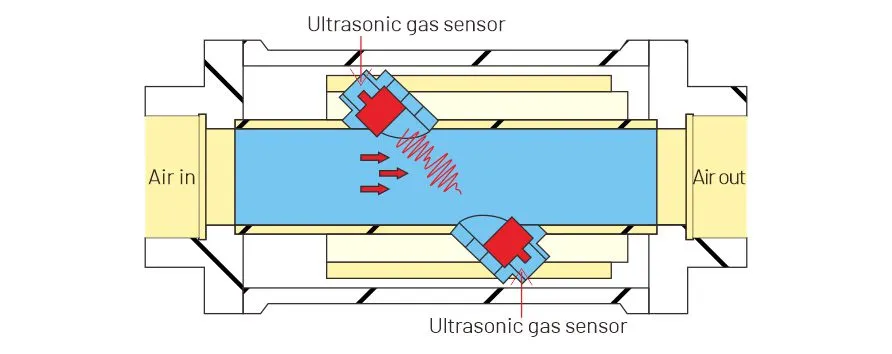
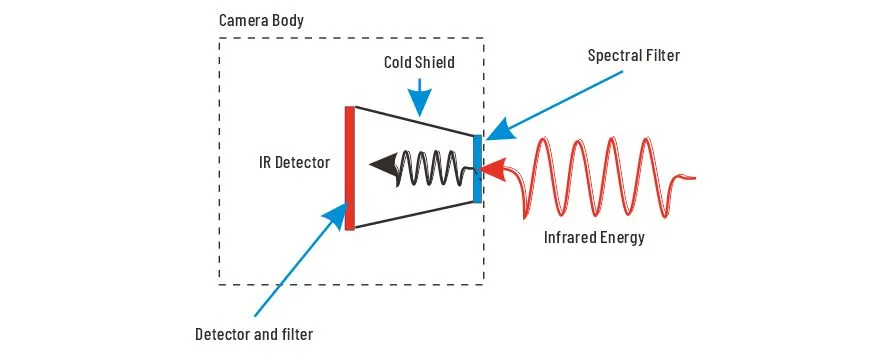

Methane is a potent greenhouse gas with a global warming potential significantly higher than carbon dioxide. Methane gas sensing helps mitigate climate change and protect the environment.

Many countries are implementing stricter regulations on methane emissions. Effective methane detection ensures companies comply with these regulations, avoiding penalties and fostering a positive public image.

Methane leaks can pose serious safety risks, including fire and explosion hazards. Prompt methane detection and repair of leaks enhance safety for workers and surrounding communities.

Identifying and addressing leaks in real-time reduces waste and improves the efficiency of oil and gas operations, which not only saves costs but also conserves valuable resources.
Contact Cubic Sensor to Explore Innovative Methane Gas Sensing Solutions!
 inquiry@gassensor.com.cn
inquiry@gassensor.com.cn
 +86-27-81628827
+86-27-81628827
 Fenghuang No.3 Road, Fenghuang Industrial Park, Eastlake Hi-tech Development Zone, Wuhan, 430205, China
Fenghuang No.3 Road, Fenghuang Industrial Park, Eastlake Hi-tech Development Zone, Wuhan, 430205, China